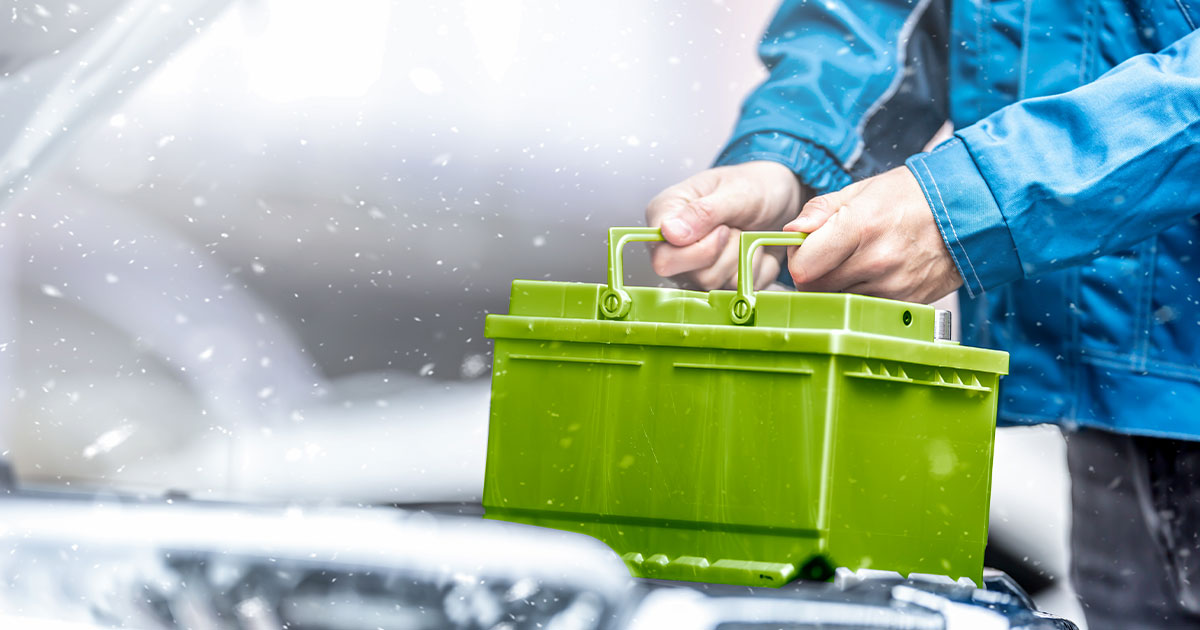
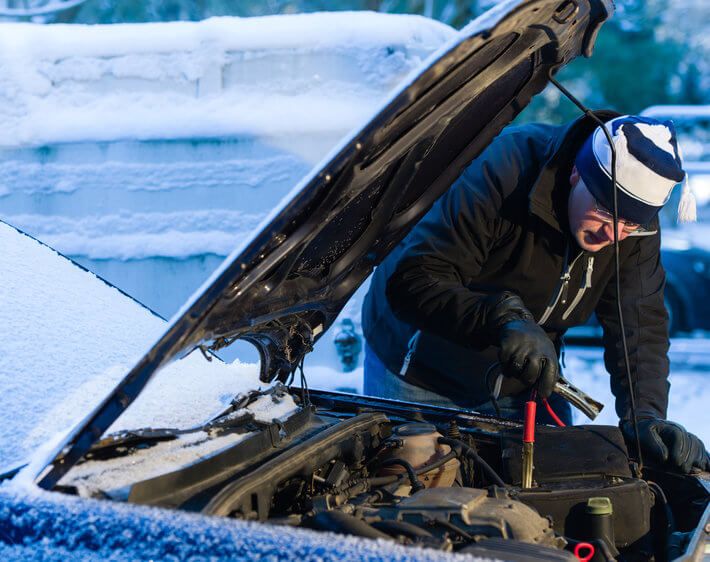
Understanding Cold-Cranking Amps (CCA)
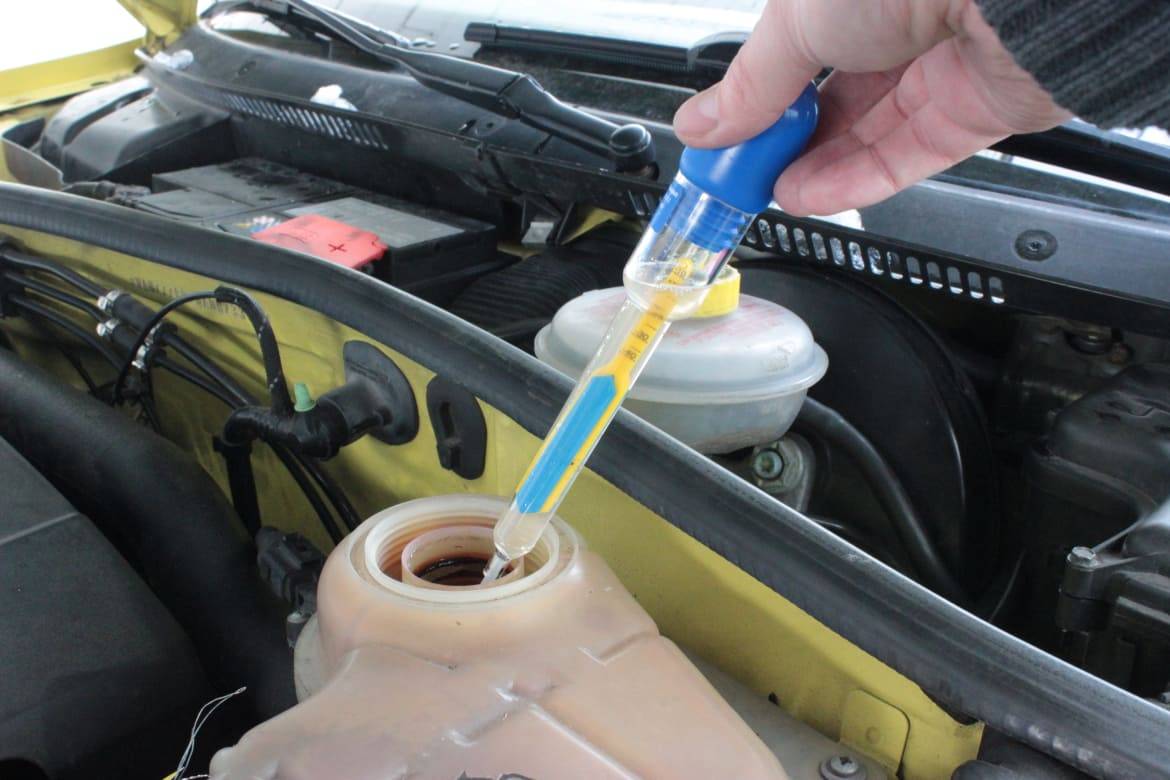
Learn what CCA ratings mean for winter starting performance, understand how cold temperatures reduce available battery power dramatically, select batteries with adequate CCA for Canadian climates and your specific vehicle requirements, compare marine-grade and AGM batteries for enhanced cold performance, and invest in quality batteries that will reliably start your vehicle even in extreme cold.